Jobs and Wages in Chicago's Industrial Corridors
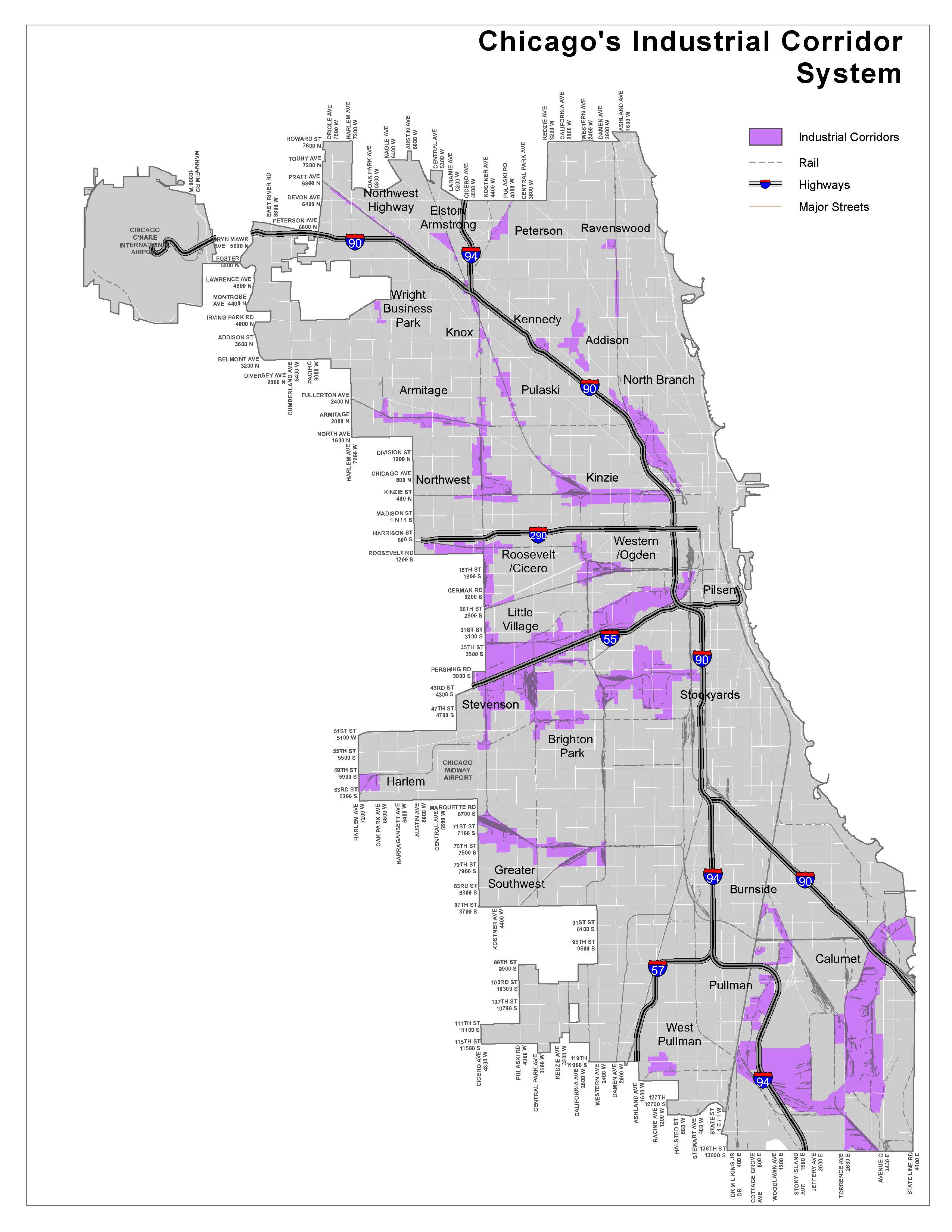
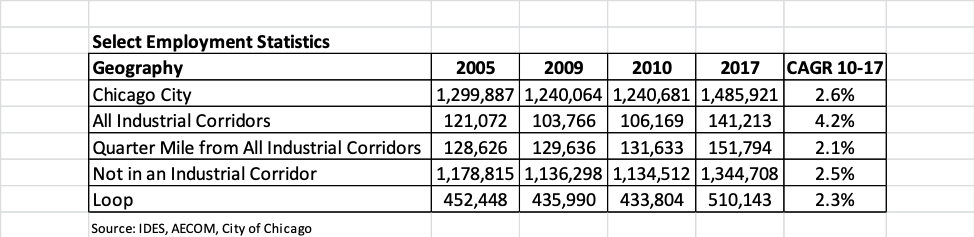
Chicago’s Industrial Corridor SystemChicago’s Industrial Corridor system is a collection of 26 contiguous geographic areas ranging in size from 70 acres to 3,500 acres. Built over the course of 150 years in proximity to the well-developed transportation network, the system is an essential part of the region’s infrastructure because it provides a stable landscape for new and expanding manufacturers, wholesalers, and distribution companies to operate. Chicago’s Industrial Corridor system is an essential element in the regional industrial ecosystem. This economic ecosystem was, and continues to be, inhabited by a diverse array of companies that continually move around within the industrial landscape, while others move in and out, and others incubate their businesses and skills nearby. The Chicago Department of Planning and Development, in conjunction with AECOM Technical Services, conducted an analysis of employment data acquired from the Illinois Department of Employment Security. The analysis looked at employment and wage growth in industrial corridors and the quarter-mile surrounding the corridors. The analysis shows that Industrial Corridors act as jobs centers and the number of jobs is growing. Employment growth within industrial corridors outpaced employment growth for the City as a whole. Jobs in industrial corridors have grown 4.2 percent between 2010 and 2017 compared to 2.6 percent growth citywide and 2.3 percent in the Loop during the same period. Industrial Corridors have a net positive impact on job growth in areas just outside their boundaries as well. Employment grew by 2.1 percent in areas within a quarter-mile of the Industrial Corridor boundaries. In fact, approximately 23 percent of jobs added in Chicago between 2010 and 2017 were located within a quarter-mile of industrial corridors, and in total numbers, account for nearly 20 percent of all jobs in the City of Chicago.
The landscape of these corridors is constantly changing. The list of corridors at right includes links to corridor specific data that demonstrate the enduring presence of industrial and manufacturing companies. The data also shows the diversity of employment throughout the system. |
Corridor DataIndustrial Corridor System-Wide
|
Methodology
In 2018, DPD gained access to the Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) provided by the Illinois Department of Employment Security (IDES) through a shared data agreement. This data includes employment counts from 2005- 2017, industry classification and wage data used to compile the data summaries for each of the corridors.
The analysis was completed in early 2020 prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which altered economic conditions in all sectors, including industrial. DPD is working with other governmental agencies and stakeholders to assess and measure the impacts of the pandemic on the Chicago economy. As part of this work, DPD will update these employment and wage statistics when 2020 data is made available by IDES, and will continue to do so on an annual basis.